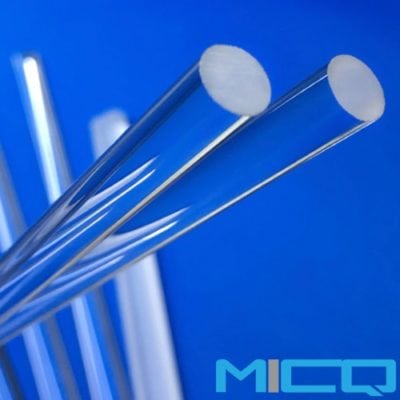
Fused Quartz Glass Rod
Fused quartz rod is a common shape of quartz glass. It is also a basic quartz glass material. It can be reprocessed into other quartz glass appliances or parts for various purposes. In optical applications, quartz rods need to have high-purity silica and be free of bubbles and extremely few impurities. In physical and chemical applications, it is usually only needed to be resistant to high temperature and corrosion, so it is allowed to have a few small bubbles.
Does the size and shape of the quartz rod influence its effect?
A quartz rod is a commonly utilized experimental apparatus, employed primarily for the preparation, heating, mixing, stirring and other experimental operations. The dimensions and shapes of the quartz rod are two crucial factors of its operational efficacy, exerting a great impact on the outcomes of the experimental procedure. The following will be detailed from two aspects of quartz rod size and quartz rod shape.
- Influenceof quartz rod size on its operation effect
Quartz rod size refers to the length and diameter of the quartz rod. The size of the quartz rod has a direct impact on the experimental operation effect, and the following will be discussed in detail from the two aspects of length and diameter.
- The influenceof the length of quartz rod
The length of quartz rod mainly influence the effect of mixing and stirring. Generally speaking, the longer the length of the quartz rod, the greater the range of mixing and stirring. If you need to mix or stir a relatively large solution or reagent mixture, you should choose a longer quartz rod to ensure adequate mixing. If you need to mix or stir a relatively small solution or reagent mixture, you can choose a quartz rod with a shorter length. The length of the quartz rod is also related to the depth of the bottle or container, and choosing a quartz rod with a suitable length can effectively reduce the difficulty of operation.
- The influenceof the diameter of quartz rod
The diameter of the quartz rod exerts a significant influence on the heating effect, with thicker rods demonstrating superior heating capabilities. This is due to the fact that a quartz rod with a larger diameter has a smaller surface area in comparison to a quartz rod with a smaller diameter, under identical heating conditions. A smaller surface area represents a reduction in heat emission, thus resulting in a relatively superior heating effect. Furthermore, quartz rods with smaller diameters are susceptible to deformation during the heating process, while quartz rods with larger diameters are more heat-resistant.
In general, the selection of quartz rod length and diameter should be based on different experimental requirements. Prior to utilization, it is imperative to ascertain the dimensions of the container and the operational material, and to meticulously determine the length and diameter of the quartz rod, in order to guarantee optimal outcomes.
- Influenceof quartz rod shape on its operation effect
The shape of quartz rod mainly affects the mixing, stirring and moving effect during the experimental operation. The influence of quartz rod shape on experimental results will be elaborated from two aspects of the rod shape and the end shape.
- The influence of the rod shape
There are two common quartz rod shapes: round rod and hexagonal rod. Hexagonal rods have more edges and corners, which facilitates the gripping of objects during mixing, stirring and transportation, thereby enhancing the efficiency of the mixing process. The round rod operates with less friction and is more difficult to grasp objects, resulting in a comparatively simple operation. It is therefore recommended that hexagonal rods be selected for special mixing and stirring experiments in order to obtain optimal results, whereas round rods should be selected for smooth operations.
- The influence of the end shape of the rod
The end shape of the quartz rod is also an important factor affecting the experimental operation effect. The end shapes of quartz rods can be broadly classified as notched, round and conical. These three shapes of quartz rods are employed in different ways and each possesses distinctive advantages.
The quartz rod with a notched end is often used to mix two different volumes of solution or reagent mixtures, and its end shape allows the two solutions to be better mixed and does not separate the two solutions.
The quartz rod with a round end is appropriate for the mixing of reagent mixtures with a higher consistency. It facilitates the outward displacement of the reagent mixture while simultaneously ensuring uniform stirring, thereby achieving the desired mixing effect.
The conical end of the quartz rod is conducive to the filling of samples, as the tapered end allows for more precisely fitting materials to a narrow bottleneck. Furthermore, the device can be utilized for the mixing and pulverisation of solid samples.
In conclusion, the dimension and shape of the quartz rod directly influence experimental effect, so it is necessary to choose a suitable quartz rod in different experimental operations. Selecting a unsuitable rod may lead to varying degrees of impact on experimental operations and the accuracy of experimental data. Furthermore, attention must be given to material selection, cleaning, and maintenance when utilizing quartz rods to ensure sustained optimal performance.
Optical Quartz Light Guide Rod
Large Size Quartz Rod
Capillary Quartz Rod
Quartz Wafer-Quartz Boat
CNC Machined Quartz Parts
Quartz Rod Deep Processing
For prompt quotation, please contact us at below form.
Application:
Chemical Industries
Electric Light Source
Laboratories
Medical equipment
Metallurgy
Optical
Photovoltaic
Photo communications
Research
Schools
Semiconductor
Solar