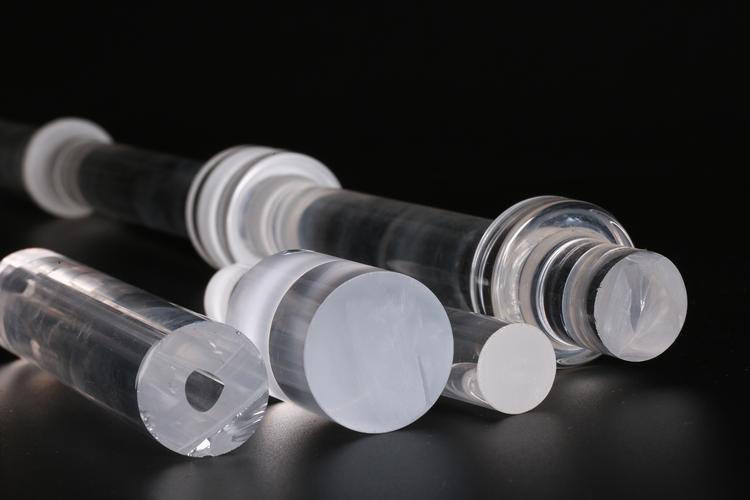
Quartz glass rods are primarily utilized in laboratories, facilitating the stirring of liquids without causing harm to the operator or the tested liquid. As employed with increasing frequency in laboratories, stirring rods can be classified according to their composition into numerous categories. Quartz glass rods, for example, represent one such category, which possess the following functions:
- Uniform the dispersion of heat
- Transferliquids and solids
- Used for diversion of liquids in situations such as filtration
- Used for stirring in the case of dissolutionand evaporation
- Initiatea reaction, such as igniting red phosphorus
Precautions of quartz glass rod
- The stirring process should be conducted in a single direction, either clockwise or counterclockwise.
- It is important to avoid excessive stirring, as this could result in the breakage of the glass rod or the container (such as a beaker).
- The glass rod is not permitted to hit the wall or the bottom of the containerduring stirring, andany sound generated by stirring is forbidden.
In a broad sense, quartz also includes high-temperature quartz and coesite. However, as one of the main rock-forming minerals, quartz generally refers to low-temperature quartz, which is a widely distributed mineral within the quartz group. Pure quartz is colorless and transparent. However, some quartz exhibit a variety of colors due to the presence of trace pigment ions, finely dispersed inclusions or color centers, which could reduce the transparency of the quartz. Quartz is a mineral composed of silicon dioxide, and the chemical formula is SiO2. Quartz block, also known as silica, is the primary raw material for the production of quartz sand. Additionally, it is the essential ingredient for quartz refractory and the firing of ferrosilicon. The material displays a glassy lustre, and the fracture exhibits a greasy lustre. The main component of quartz is SiO2, which is generally colorless and transparent. However, due to the presence of minor impurities, it can also form translucent or opaque crystals with a hard texture.