The Reasons and Prevent Methods for the Occurrence of Microbubbles on Quartz Crucibles
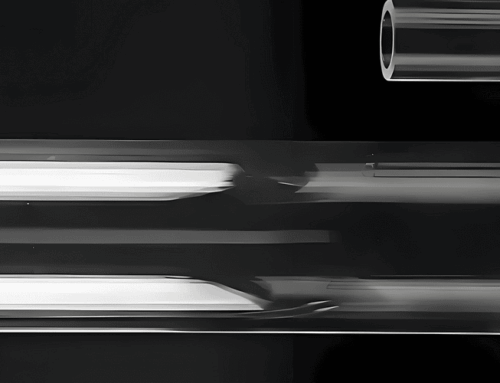
The quartz crucible exhibits translucency and features a dual-layer structure consisting of an outer layer, also referred to as the bubble composite layer, which is opaque with a high bubble content, and an inner layer, known as the bubble-free layer, which is transparent without any bubbles and has a thickness of 3–5 mm. The lifespan of the crucible is influenced by the control of microbubble content in its transparent layer. During high-temperature melting processes, the inner surface in contact with the silicon liquid gradually dissolves into it. As microbubbles within the transparent layer continue to expand, those near the innermost surface rupture, releasing quartz microparticles and microbubbles into the silicon liquid. These impurities flow throughout the entire silicon melt in the form of microparticles and microbubbles alongside silicon liquid, directly impacting silicon crystallization (overall rod yield, crystallization rate, heating duration, processing cost) and single crystalline silicon quality (perforated pieces, black chips).
During the molding process of the quartz crucibles, due to the extremely high temperature, the liquid inclusions on the quartz surface will absorb and expand, making the surface of the crucible full of bubbles and cracks, and affecting the quality of the crucible. As the inner wall of the quartz crucible is in contact with the silicon melt, the presence of bubbles in the inner wall at high temperatures will result in the release of gas and impurities from the crucible into the melt. This will have an adverse effect on the growth of single crystalline silicon.
The reasons for the occurrence of microbubbles:
There is air between the quartz particles, and gas liquid inclusion within the quartz sand.
Prevent methods:
Optimize the production process of quartz crucibles, and adjust the process parameters duringthe melting of the crucible By precisely adjusting and coordinating each parameter, reduce the gas between quartz sand being wrapped in the transparent layer;
Choose thehigh-quality quartz sand with a low content of gas-liquid inclusions, in order to facilitate the control of gas-liquid inclusions in the raw materials at a lower level.